Breast Reconstruction
Breast reconstruction is the procedure to restore the breast in women who have undergone or must undergo a total or partial mastectomy.
The different techniques for breast reconstruction, as well as medical supplies used in them, have evolved a great deal during the last few years. Although reconstruction can not compensate for the lost of breast perfection, it can recreate a breast similar in shape, size and texture to the non operated breast.
Indications
Breast reconstruction can be performed in any patient who has to undergo or have already undergone a total mastectomy (unilateral or bilateral) or partial mastectomy(lumpectomy, quadrantectomy).
The reconstruction can be carried out at the same time as the breast cancer operation (immediate surgery) or later (delayed surgery), approximately one year after treatment start.
This decision is determined by a multidisciplinary team, among them the most import being the oncologist and gynecologist.
First Visit
A personal visit is the first step for any woman who is thinking about a breast reconstruction.
Dr. Saez will ask about your general health, the additional treatment received (specially radiotherapy) and your expectations.
Dr. Saez will examine your breasts, assess the type of scar and its characteristics (hardness, thickness , colour) , the quality of the skin (thickness, elasticity, quantity, colour) and the muscle (pectoralis major), which have been left after mastectomy. Dr. Saez will also assess the shape and size of the contralateral breast in cases of unilateral mastectomy.
From an individualized evaluation Dr. Saez will explain the technique and the results that can be achieved by surgery.
Procedure
There are several techniques for breast reconstruction depending on the needs of each patient.
Several factors come into play when opting for one or the other technique, most notably the general health, disease’s prognosis, the shape/ size of the breast, skin/tissue remaining after the operation, lifestyle and patient wishes.
Reconstruction techniques for a total mastectomy:
• Breast reconstruction with implants.
• Reconstruction with autologous tissue.
• Reconstruction with mixed techniques.
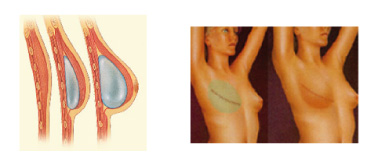
• RECONSTRUCTION WITH BREAST IMPLANTS:
Breast reconstruction with implants, the most practiced worldwide, is the best choice for a significant portion of patients. This method places a breast implant under the pectoral muscle through the mastectomy scar. In the majority of cases it is necessary to expand the chest skin with an inflatable expander before the final implant is placed to reproduce a natural looking breast in a second operation.
These operations are done under general anaesthesia, and the usual stay at the clinic is 24 hours. The nipple and areola are reconstructed later using local anaesthesia on an outpatient basis.
This method is especially useful if no new scars is desired. However, it is not entirely suitable if the skin has been damaged, especially if you have received radiotherapy.
• RECONSTRUCTION WITH AUTOLOGOUS TISSUE:
Breast reconstruction with autologous tissue (patient’s own tissues) is chosen in those cases where patient have received radiotherapy after mastectomy. The reason for not being a good candidate for prosthetic reconstruction is that it so frequently ends with bad results.
Reconstruction with autologous tissue consists of tissue mobilization from other parts of the body such as the back or abdomen to recreate the breast.
Used as a tissue donor:
– The latissimus dorsi muscle from the back.
– The TRAM or DIEP flap from the belly.
These techniques are more complex than those which employ cutaneous expansion, creates new scars in the donor area and the recovery period is longer than for implants. However, the aesthetic result is superior and there are no problems with the implants (capsule formation).
These techniques are also performed under general anaesthesia; the usual stay at the clinic is between 4 and 7 days.
The nipple and areola are reconstructed later using local anaesthesia and on an outpatient basis.
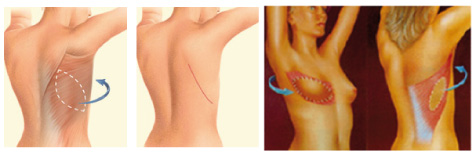
• RECONSTRUCTION WITH THE LATISSIMUS DORSI MUSCLE OF THE BACK:
It mobilizes skin, fat and muscle from the back area to reconstruct the breast.
Because the tissue from the back is thin, it is usually necessary to use a breast implant or filled with fat (lipofilling) to provide a greater volume and a give more the breast natural shape.
It is a reliable method, suitable for most patients, but it leaves a new scar in the back.
RECONSTRUCTION WITH THE TRAM and DIEP FLAP FROM THE BELLY:
The TRAM and DIEP flap mobilize tissue from the abdomen to reconstruct the breast. It is indicated in women who have excess fat in the abdominal region.
The difference between these two flaps is the preservation of the rectus muscle of the abdomen and the need for microsurgery in the case of DIEP. Vascularization is completely separate from their original site and is transplanted to the chest by connecting the blood vessels in the area with microsurgical techniques, being this technique more complex. In the TRAM flap is not preserve the rectus muscle of the abdomen (so it requires an abdominal mesh) and tissue is still attached to its original site, keeping its vascularization, being transferred to the breast using a tunnel that runs under the skin.
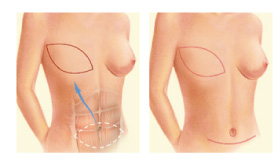
When tissue of the abdomen is mobilized, there is the added benefit of improving abdominal contour (as if it were an aesthetic abdominoplasty).
• RECONSTRUCTION WITH MIXED TECHNIQUES:
This technique is particularly suitable in patients who have undergone radiotherapy and do not want a complex surgery as in the case of autologous reconstruction.
It consists of combining the placement of a prosthesis with fat injection from the same patient. Fat Injection acts on the skin and scars, improving its quality and elasticity. In these cases, it is started with a liposuction to obtain the fat, resulting in improved body contour at the same time. The fat is injected under the skin of the chest, and inside the mastectomy scar. Later, once elasticity and skin thickness is improved, implant expander is introduced in a second time.
With this combined method a more natural contour is achieved.
Post-op care
Although each person’s recovery is different, it is common to follow the next steps:
After the operation the usual stay at the clinic is 2 to 5 days, depending on the operation, thereafter the patient can be discharged.
THE FIRST DAY:
• It is advisable to rest with the chest slightly lifted. You should not manipulate the bandage.
DURING THE FIRST WEEK:
• The bandage will be removed after 3 or 4 days, and you will have to wear a special bra.
• You must take moderate rest, especially the arms.
AFTER THE FIRST WEEK:
• You can progressively start to wok and return to normal activity.
• The stitches will be removed (although we don’t usually use visible sutures).
AFTER THE FIRST MONTH:
• Inflammation will be reduced and you will start to see the final result more defined.
• You can do more vigorous exercises.
• Scars start to blend in with the skins natural tone better over time.
Results
Breast reconstruction is one of plastic surgery interventions that has highest percentage of satisfied patients.
Reconstruction has no effect on the recurrence of the disease, nor interfere with chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Neither interferes with subsequent studies that may be necessary in posterior revisions.
The results achieved are maintained for many years. However, you must remember that your breasts are not immune to the effects of fluctuations in weight or age.
It is advisable to take care of skin by moisturising, and make some physical exercise.
